Federal Policy
Home > Our Work > Federal EV Policy > CFI Tools & Resources Hub
Charging and Fueling Infrastructure (CFI) Discretionary Grant Program Resources Page
UPDATE: On January 11, 2024, the first round of CFI awards was announced. To learn more, read our press release, visit our Trends and Takeaways page, and watch the recording of our “Charging and Fueling Infrastructure Awards: Next Steps and Best Practices” webinar produced in collaboration with Forth.
Table of Contents
The Charging and Fueling Infrastructure (CFI) Grant Program is a federal grant program focused on deploying EV charging on publicly accessible corridors and public roadways, increasing accessibility to EV charging across urban and rural areas alike. The first tranche of $700M is funded through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, divided into two program funds focused on Community Charging and Fueling Grants (Community Program) and Alternative Fuel Corridors (Corridor Program). Overall, these grant programs will strategically deploy EV charging stations across various urban and rural communities, increasing publicly accessible charging in downtown areas, underserved and disadvantaged communities, local neighborhoods, and other convenient charging locations. We recommend reading through our Top 10 Takeaways Guide for further understanding of the program’s aim, scope, and functionality.
How Do I Build My Project?
The Federal Highway Administration has provided an overview of the CFI Grant. The EC has also prepared a Guidance Table to breakdown comparison between the Community Grant Program, Corridor Grant Program, and their specific focuses.
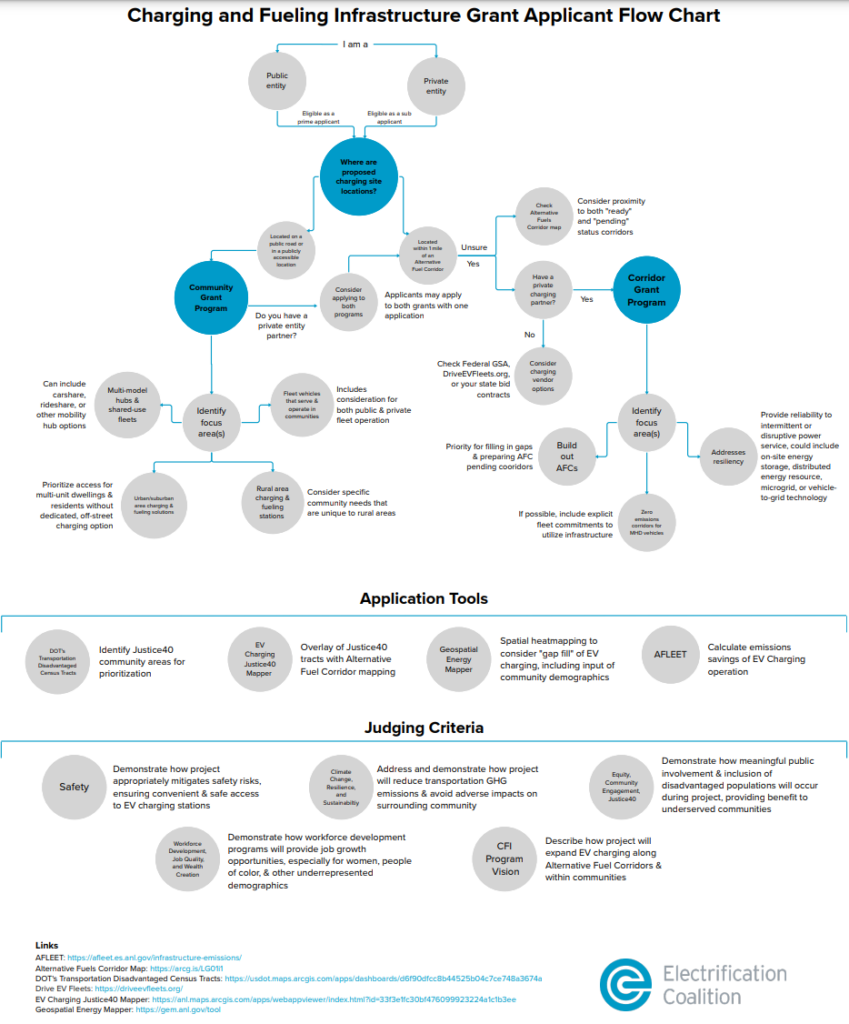
The EC has prepared a Decision Tree matrix to help potential applicants navigate through the grant design process!
Click the decision tree below to open in PDF format.
Looking to streamline your CFI grant application process? Check out our CFI Application Toolkit, which contains several relevant tools and resources to reduce application time and enhance the quality of your application.
CFI 101 Webinar
With the help of Steve Lommele from the Joint Office of Energy and Transportation and our partner Forth, we offered an overview of the CFI Program and explained how cities, states, and private entities can structure their applications for the $700 million first round of funding.
Here to Help!
The EC is providing informational resources for helping applicants navigate the grant application process. Our staff are available at infrastructure@electrificationcoalition.org if you have any specific questions or wish to discuss further support our organization can provide for educational and community engagement activities to support EV and charging education allowed under the CFI Grant Program.